3D Printing Business Insights And Practical Steps

The very first object made by a 3D printer was just a small cup. From such a simple start, 3D printing has grown into a key part of how things are made and designed today.
This post explores the exciting field of 3D printing business, where cutting-edge technology meets endless imagination. It's a look into how 3D printing is shaping businesses beyond machines and their capabilities.
We'll look at different types of 3D printing and see how this technology can be a powerful tool for businesses. Read on to uncover a world where ideas turn into real, tangible creations in business and more.
Table of Contents
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, a transformative technology, stands at the forefront of manufacturing and design innovation. It's a process where digital 3D models are turned into physical objects by adding material layer by layer.
This technology has revolutionized prototyping and manufacturing across various industries due to its ability to create complex designs with precision and speed.
Not only has it become a tool for large-scale production, but it's also accessible to small businesses and hobbyists, fueling creativity and entrepreneurial spirit.
What are the steps in 3D printing?
3D printing is revolutionizing how we create and manufacture objects, from small custom pieces to large-scale production. This guide outlines the key steps involved in the 3D printing process, an essential knowledge base for anyone looking to start a 3D printing business.
Whether you're contemplating business 3D printing ideas or curious about how much 3D printing businesses make, understanding these steps is key.
1. Design the 3D Model
The foundation of any 3D printing project lies in designing a precise 3D model. This model acts as a blueprint, guiding the printer. It’s typically created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, where the designer can meticulously sculpt their vision. Key aspects include:
- Ensuring design accuracy for functional parts or aesthetic appeal.
- Considering the print's feasibility and structural integrity.
- Optimizing the design to minimize material use and print time.
Businesses exploring 3D printed business cards or intricate models must pay extra attention to detail at this stage.
2. Choose the Right Material
Material selection dramatically influences the final product's quality and function. Each material offers unique properties like strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance. Important considerations include:
- Matching material properties with the print’s intended use.
- Understanding the cost implications for a 3D printing business.
- Recognizing environmental factors and material sustainability.
For those looking into 3D printing business ideas, choosing versatile materials can open up diverse product opportunities.
3. Set Up the 3D Printer
Setting up the printer is more than flipping a switch. It involves calibrating the machine for optimal performance. Essential steps include:
- Ensuring the build platform is level.
- Selecting the correct printing parameters like temperature and speed.
- Loading the material and verifying its compatibility with the printer.
Businesses should focus on thorough setup to avoid costly errors and waste.
4. Begin the Printing Process
Starting the print is a pivotal moment. The printer interprets the 3D model into layers and begins constructing the object layer by layer. Vital points here are:
- Confirming the first layer adheres well to the build platform.
- Watching for potential issues in the early stages of printing.
- Understanding that complex prints might require support structures.
For a business, efficient printing processes can impact how much 3D printing businesses make.
5. Monitor the Print Progress
Monitoring is crucial for ensuring quality and identifying issues early. Key aspects involve:
- Regularly checking for print errors or material issues.
- Adjusting settings in real-time if needed.
- Ensuring the printer maintains optimal operating conditions.
6. Remove the Completed Print
Once printing concludes, safely removing the print is essential. This involves:
- Allowing the print to cool down to avoid deformation.
- Carefully detaching the print from the build platform.
- Inspecting the print for any immediate quality issues.
Removal techniques can vary, depending on the printer and material used.
7. Post-Processing of the Print
Post-processing can transform a print from a raw state to a finished product. This stage might include:
- Cleaning off any support material.
- Sanding or smoothing the surface for aesthetics.
- Applying paint or sealant for protection and visual appeal.
Post-processing can significantly improve the value and appeal of the product.
Types of 3D Printing
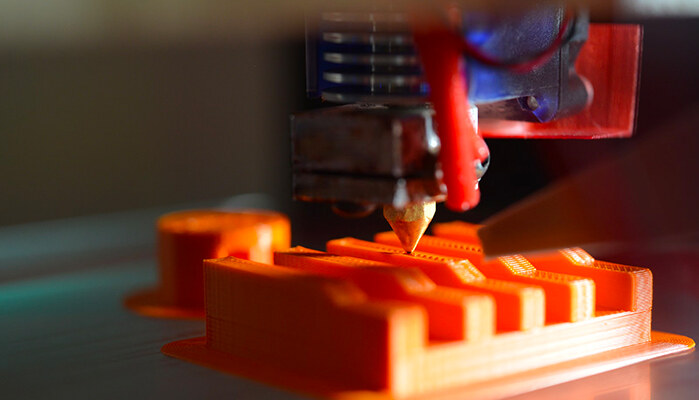
1. FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM is one of the most common 3D printing techniques, known for its cost-effectiveness and ease of use. It works by extruding thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle, layer by layer, to create an object. Key aspects include:
- Material Variety: Uses a range of thermoplastic filaments like ABS, PLA, and PETG.
- Applications: Ideal for prototyping, hobbyist projects, and educational purposes.
- Benefits and Limitations: Offers great material choice and ease of use but limited in resolution and finish quality.
2. SLA (Stereolithography)
SLA, the first 3D printing technology developed, uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process known as photopolymerization. Points to note:
- Precision: Known for high accuracy and smooth surface finishes.
- Materials: Utilizes photosensitive resins.
- Usage: Commonly used for detailed prototypes, jewelry, and dental applications.
- Pros and Cons: Provides excellent detail and finish but is limited by smaller build volumes and material brittleness.
3. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS involves the use of a laser to sinter powdered material, binding it together to form a solid structure. It’s distinct for:
- Material Flexibility: Works with a range of materials, including nylon, glass-filled, and metals.
- Strength and Durability: Produces robust and functional parts.
- Application Scope: Used in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
- Advantages and Challenges: Offers strong and durable parts with no need for support structures, but the process can be expensive and requires post-processing.
How to Start a 3D Printing Business
Starting a 3D printing business requires a blend of technical knowledge, market insight, and strategic planning. Each of these steps contributes to building a successful business in this innovative field.
Here are some fundamental steps on how to start a 3d printing business:
1. Master 3D Printing Technology
Before getting into the business, it's critical to have a strong grasp of 3D printing technology. This involves understanding how printers work and also staying updated with the latest advancements in the field. Key points include:
- Learning about different 3D printing technologies and materials.
- Gaining practical experience by working on various 3D printing projects.
- Keeping abreast of industry trends and technological innovations.
This knowledge base will be instrumental in guiding your business decisions and operations.
2. Conduct Market Research
Understanding the market is vital for any business, and for a 3D printing business, it's no different. Market research helps you identify your niche, understand customer needs, and scope out the competition. Essential aspects include:
- Identifying potential customer segments and their specific needs.
- Analyzing competitors and their offerings.
- Assessing the demand for different types of 3D printed products.
Informed market research can lead to more effective business 3D printing ideas.
3. Develop a Business Plan
A well-thought-out business plan is the roadmap for your venture. It outlines your business goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. Key elements to include are:
- Defining your business model and value proposition.
- Outlining financial projections and funding requirements.
- Detailing industry reports, marketing, and operational strategies.
A robust business plan can be a deciding factor in how much a 3D printing business makes.
4. Buy Equipment
Selecting the right 3D printing equipment is pivotal. This decision should align with your business objectives and budget. Points to consider:
- Choosing printers that match your quality requirements and production capacity.
- Considering the cost of printers and ongoing material expenses.
- Evaluating the ease of use and maintenance of the equipment.
The right equipment lays the foundation for the quality and efficiency of your products.
5. Choose a Sales Platform
Your sales platform is where your customers will interact with your business. Whether you choose an online marketplace, a dedicated e-commerce website, or a physical store, it should align with your target market. Important considerations include:
- Evaluating different platforms for their reach and compatibility with your products.
- Assessing the costs associated with each platform.
- Ensuring a user-friendly experience for your customers.
Choosing the right platform can significantly impact your business's visibility and sales. Alibaba.com is a great example of an online marketplace that caters to a wide range of products and has a global reach.
6. Market Your Business
Effective marketing is key to attracting and retaining customers. It involves promoting your products while also building a brand. Key strategies include:
- Utilizing digital marketing tools like social media, SEO, and email marketing.
- Participating in trade shows and networking events.
- Building a strong online presence with engaging content.
A well-executed marketing plan can elevate your brand and drive business growth.
How Much Does It Cost to Start a 3D Printing Business?

Starting a 3D printing business requires a clear understanding of the initial costs involved. These expenses can vary widely based on the scale and scope of your business. Key cost factors include:
- 3D Printers: The price of 3D printers ranges significantly, from a few hundred dollars for basic models to several thousand for advanced machines.
- Materials: Filaments, resins, or powders used in printing can also vary in cost, depending on their quality and the quantity purchased.
- Software: Investing in quality design and slicing software is essential, with prices varying based on functionality and licensing terms.
- Workspace: Renting or owning a space for your operations, if not working from home, adds to the cost.
- Marketing and Website: Budget for branding, marketing, and setting up a professional website to attract customers.
- Training and Miscellaneous: Consider costs for training, maintenance, utilities, and other miscellaneous expenses.
Overall, the cost to start a 3D printing business can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, tailored to your business model and goals. It’s important to plan your budget carefully, considering both initial investments and ongoing operational costs.
Conclusion
3D printing stands out as a brilliant example of human creativity and the ability to adapt. It's a driving force for change in the way we make and design things, opening up new possibilities in many areas.
Regardless if you're thinking about starting your own 3D printing business or just amazed by what this technology can do, remember that the future of making things isn't simply being planned; it's being printed, one layer at a time, in small workshops and big offices everywhere. What part will you play in this ongoing story of innovation?
Start Selling on Alibaba.com
Transitioning into how businesses can leverage these technologies, one avenue is through platforms like Alibaba.com. This global marketplace connects sellers with buyers worldwide, offering a vast audience for 3D printed products and services.
Starting on Alibaba.com can be a strategic move for 3D printing businesses looking to expand their reach and tap into new markets. It offers an opportunity to showcase innovative products and services to a global audience, potentially boosting sales and business growth. Try it for free here.
FAQ
Why start a 3D printing business?
Starting a 3D printing business offers numerous advantages. It allows you to tap into a growing market where the demand for customized and unique products is rising. With 3D printing, you have the flexibility to create complex designs that are not possible with traditional manufacturing methods. This technology also reduces material waste, making it a more sustainable choice. Additionally, it opens up opportunities in various sectors including medical, automotive, and fashion, providing a broad potential customer base.
What types of products can a 3D printer create?
Yes. 3D printers are incredibly versatile and can create a diverse array of items. This includes everything from simple household objects to complex components used in automotive and aerospace industries. In the medical field, 3D printers are used to create custom prosthetics and dental implants. In the consumer space, they're employed for making jewelry, toys, and home decor. The only real limits are the size of the printer and the materials used.
How do I ensure the quality of my 3D-printed products?
Ensuring the quality of 3D-printed products involves several key steps. First, it's important to use high-quality materials and a reliable 3D printer. Regular maintenance of your printer is also crucial to prevent defects. The design process should include precise measurements and considerations for the specificities of 3D printing. During printing, closely monitor the process to detect any issues early on. Finally, post-processing steps like sanding and painting can significantly enhance the final product's appearance and durability.
Start your borderless business here
Tell us about your business and stay connected.
Keep up with the latest from Alibaba.com?
Subscribe to us, get free e-commerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
















